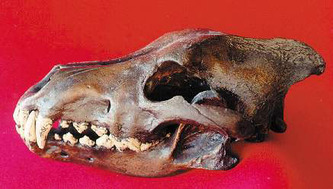
Here you can find those wolf species which are unfortunately extinct.
Dire Wolf (Canis dirus):

The Dire Wolf, is an extinct carnivorous mammal of the genus Canis, and was most common in North America and South America from the Irvingtonian stage (1.8 million years ago) to the Rancholabrean stage (0.011 million years ago) of the Pleistocene epoch. Canis dirus existed for approximately 1.69 million years.
Although it was closely related to the Gray Wolf and considered a sister species, Canis dirus was not the direct ancestor of any species known today. Unlike the Gray Wolf, which is of Eurasian origin, the Dire Wolf evolved on the North American continent, along with the Coyote a wide variety of very large mammals that lived during the Pleistocene. Approximately 10,000 years ago the Dire Wolf became extinct along with most other North American megafauna.
The first specimen of a Dire Wolf was found by Francis A. Linck at the mouth of Pigeon Creek along the Ohio River near Evansville, Indiana in 1854, but most fossils recovered have been from La Brea Tar Pits in California.
Although it was closely related to the Gray Wolf and considered a sister species, Canis dirus was not the direct ancestor of any species known today. Unlike the Gray Wolf, which is of Eurasian origin, the Dire Wolf evolved on the North American continent, along with the Coyote a wide variety of very large mammals that lived during the Pleistocene. Approximately 10,000 years ago the Dire Wolf became extinct along with most other North American megafauna.
The first specimen of a Dire Wolf was found by Francis A. Linck at the mouth of Pigeon Creek along the Ohio River near Evansville, Indiana in 1854, but most fossils recovered have been from La Brea Tar Pits in California.
Kenai Peninsula Wolf (Canis lupus alces):

The Kenai Peninsula Wolf was a subspecies of the Gray Wolf and it lived in the tundra regions of Alaska.
It was a very large wolf. The determination of the species and the size of the wolf was done using recovered bones.
It was a very large wolf. The determination of the species and the size of the wolf was done using recovered bones.
Falkland Islands Wolf (Dusicyon australis):

The Falkland Islands Wolf, also known as the Warrah and occasionally as the Falkland Islands Dog, Falkland Islands Fox or Antarctic Wolf, was the only native land mammal of the Falkland Islands. This endemic canid became extinct in 1876 (on West Falkland island), the first known canid to have gone extinct in historical times. It was the only modern species in the genus Dusicyon. The most closely related genus is Lycalopex, including the Culpeo, which itself has been introduced to the Falkland Islands in modern times. It was known from both West and East Falkland, but it is unknown if the varieties were much differentiated.
The fur of the Falkland Islands Wolf had a tawny colour. The tip of the tail was white. The diet is unknown. Due to the absence of native rodents on the Falklands, its diet probably consisted of ground-nesting birds such as geese and penguins, grubs and insects, as well as seashore scavenging. It was sometimes said to have dwelt in burrows.
The fur of the Falkland Islands Wolf had a tawny colour. The tip of the tail was white. The diet is unknown. Due to the absence of native rodents on the Falklands, its diet probably consisted of ground-nesting birds such as geese and penguins, grubs and insects, as well as seashore scavenging. It was sometimes said to have dwelt in burrows.
Honshu Wolf (Canis lupus hodophilax):

The term "Japanese Wolf" (狼, Ookami) refers to two extinct subspecies of the Gray Wolf. The subspecies that the name 'Japanese Wolf' usually describes is the Honshu Wolf (日本狼, Nihon Ookami), which occupied the islands of Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu in Japan. The other is the Hokkaido Wolf. The Honshu Wolf is thought to have become extinct due to a combination of rabies, which was first reported in Kyushu and Shikoku in 1732, and human eradication. The last known specimen died in 1905, in Nara Prefecture.
Some interpretations of the Honshu Wolf's extinction stress the change in local perceptions of the animal: rabies-induced aggression and deforestation of the wolf's habitat forced them into conflict with humans, and this led to them being targeted by farmers.
There are currently eight known pelts and five stuffed specimens of the Japanese Wolf in existence. One stuffed specimen is in the Netherlands, three are in Japan, and the animal caught in 1905 is kept in the Brithish Museum. Owing to its small size (the Honshu Wolf is the smallest known variety of wolf, probably due to allopatric speciation / island dwarfing) the Honshu Wolf's classification as a subspecies of the gray wolf is disputed.
The wolf was afforded a benign place in Japanese folklore and religious traditions: the clan leader Fujiwara no Hidehira was said to have been raised by wolves, and the wolf is often symbolically linked with mountain kami in Shinto (the most famous example being the wolf kami of Mitsumine Shrine in the town of Chichibu in Saitama Prefecture).
Sightings of the Japanese Wolf have been claimed from the time of its extinction to the present day, but none of these have been verified.
Some interpretations of the Honshu Wolf's extinction stress the change in local perceptions of the animal: rabies-induced aggression and deforestation of the wolf's habitat forced them into conflict with humans, and this led to them being targeted by farmers.
There are currently eight known pelts and five stuffed specimens of the Japanese Wolf in existence. One stuffed specimen is in the Netherlands, three are in Japan, and the animal caught in 1905 is kept in the Brithish Museum. Owing to its small size (the Honshu Wolf is the smallest known variety of wolf, probably due to allopatric speciation / island dwarfing) the Honshu Wolf's classification as a subspecies of the gray wolf is disputed.
The wolf was afforded a benign place in Japanese folklore and religious traditions: the clan leader Fujiwara no Hidehira was said to have been raised by wolves, and the wolf is often symbolically linked with mountain kami in Shinto (the most famous example being the wolf kami of Mitsumine Shrine in the town of Chichibu in Saitama Prefecture).
Sightings of the Japanese Wolf have been claimed from the time of its extinction to the present day, but none of these have been verified.